JADE now supports the WebSocket communication protocol.
The WebSocket protocol enables interaction between a web client (such as a browser) and a JADE server‑side application, facilitating real‑time data transfer from and to the server. This is made possible by providing a standardized way for the JADE server‑side application to send content to the client without being first requested by the client, and allowing messages to be passed back and forth while keeping the connection open. In this way, a two‑way ongoing conversation can take place between the client and server‑side application.
The communications are done over TCP port number 80 (or 443, in the case of TLS‑encrypted connections), which is of benefit for those environments that block non-web Internet connections using a firewall.
IIS has to be correctly configured to handle incoming WebSocket connections and forward requests that will be handled by JADE to the JadeWebSocketModule (that is, the jadeWebSockets_IIS.dll native IIS module).
A JadeWebSocketModule instance loaded into an IIS worker process maps WebSocket connections to JADE application instances using URL pattern‑matching rules that yield a host (network name or IP address) and TCP port number.
The WebSocket protocol is not supported by JADE applications connected to an Apache HTTP Server.
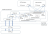
A simple message protocol is used to multiplex the WebSocket sessions and their messages over each JADE application TCP connection, as shown in the following diagram.
As IIS is typically configured to run multiple worker processes, multiple instances of the JadeWebSocketModule can be active at the same time, so JADE applications must support multiple TCP connections.
For details, see "
