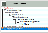
The Schema Browser in the following example contains application schemas extending down the DemoCompanySchema branch and a RootSchema subschema called LoggingPackageSchema, which provides log file services we would like to be able to use from our application schemas.
To use the log file services in LoggingPackageSchema in this hierarchy without using a package, we would have to take one of the following actions.
Insert LoggingPackageSchema into the application schema hierarchy above the first schema in which we want to use the services. This can encourage top-heavy schema hierarchies.
Make use of global instance visibility and indirect methods (for example,
By using a package, the LoggingPackageSchema facilities can be seamlessly and type-safely used by any other schema. For the purposes of this example, imagine that LoggingPackageSchema contains the LogManager, Log, and LogTagDict classes shown in the following schema file.
LogManager completeDefinition
(
referenceDefinitions
allLogs: LogTagDict explicitInverse, subId = 1, number = 1;
jadeMethodDefinitions
create() updating, number = 1001;
createLog(
logTag: String;
appTag: String;
fileName: String): Log number = 1005;
delete() updating, number = 1002;
deleteLog(log: Log io) number = 1006;
finalize() number = 1003;
initialize() number = 1004;
)
Log completeDefinition
(
attributeDefinitions
appTag: String[52] number = 2;
fileName: String[258] number = 3;
fred: Character protected, number = 5;
logTag: String[52] number = 1;
referenceDefinitions
myLogManager: LogManager explicitEmbeddedInverse, number = 4;
jadeMethodDefinitions
close() number = 1001;
create() updating, number = 1003;
delete() updating, number = 1004;
log(txt: String) number = 1005;
open() number = 1002;
)
LogTagDict completeDefinition
(
)
memberKeyDefinitions
LogTagDict completeDefinition
(
appTag;
logTag;
)
exportedPackageDefinitions
Logging
(
exportedClassDefinitions
Log
(
exportedPropertyDefinitions
appTag;
fileName;
logTag;
exportedMethodDefinitions
close;
log;
open;
)
LogManager
(
exportedPropertyDefinitions
allLogs;
exportedMethodDefinitions
createLog;
deleteLog;
)
LogTagDict
(
)
)
referenceDefinitions
myExceptionLog: Logging::Log protected, number = 2;
myLogManager: Logging::LogManager protected, number = 1;
myMsgLog: Logging::Log protected, number = 4;
myPollingLog: Logging::Log protected, number = 3;
appInit
{
appInit() updating;
begin
create self.myLogManager transient;
self.myExceptionLog := self.myLogManager.createLog('DEMO',
'ExLog', 'c:\temp\ex.log');
self.myPollingLog := self.myLogManager.createLog('DEMO',
'PollLog', 'c:\temp\poll.log');
self.myMsgLog := self.myLogManager.createLog('DEMO',
'MsgLog', 'c:\temp\msg.log');
self.myExceptionLog.open;
self.myPollingLog.open;
self.myMsgLog.open;
self.myMsgLog.log('Opened logs ' &
self.myExceptionLog.fileName & ' , ' &
self.myPollingLog.fileName & ' , ' & self.myMsgLog.fileName);
end;
}
appFini
{
appFini() updating;
begin
self.myLogManager.deleteLog(self.myExceptionLog);
self.myLogManager.deleteLog(self.myPollingLog);
self.myLogManager.deleteLog(self.myMsgLog);
delete self.myLogManager;
end;
}
appFini
{
appFini() updating;
begin
self.myLogManager.deleteAllLogs;
delete self.myLogManager;
end;
}
Although LoggingPackageSchema can also contain numerous implementation classes, we are not concerned with these in this packages usage example.
